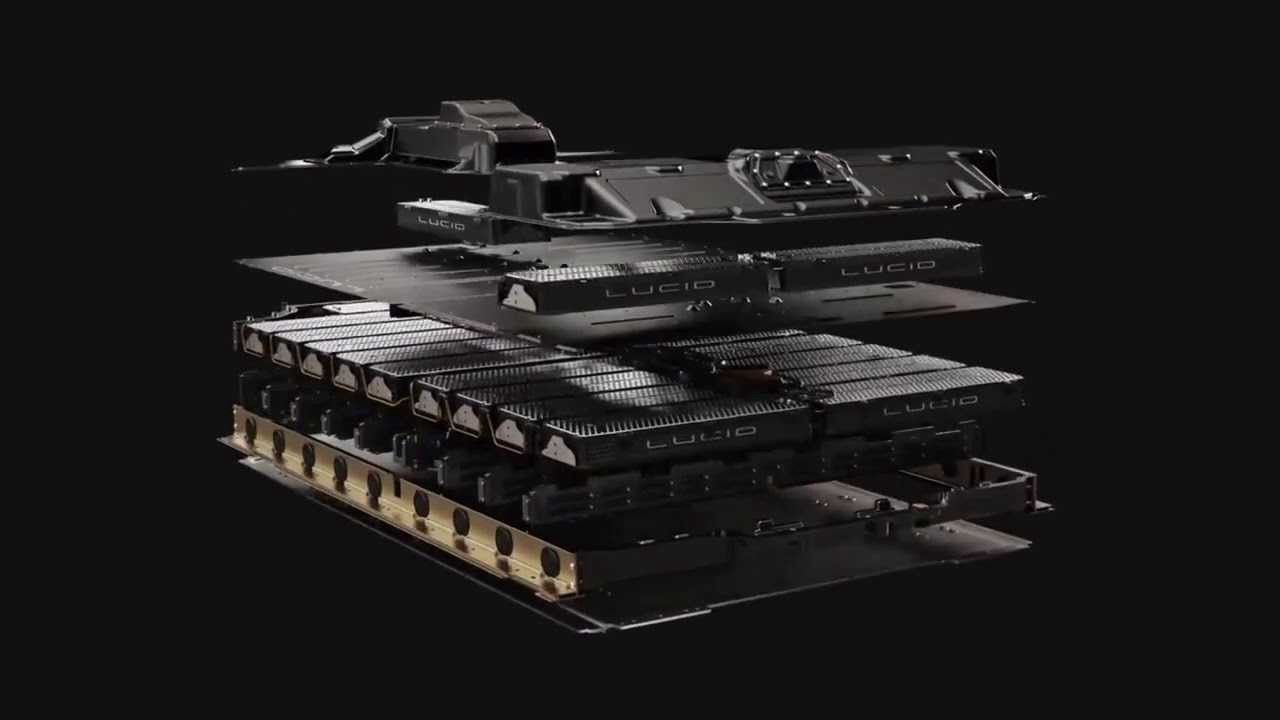
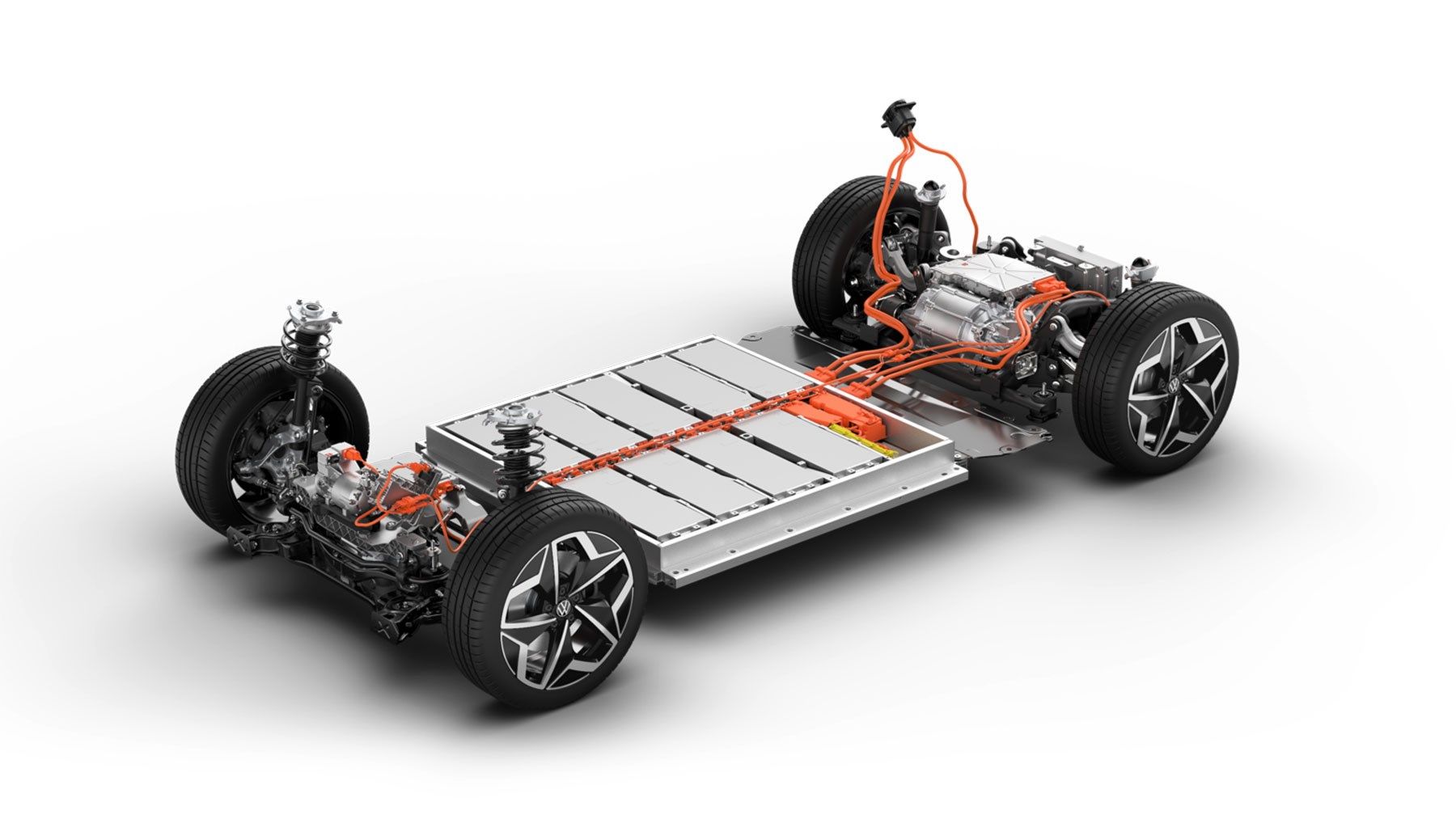
The car community, in general, is always looking to better understand existing technology so advancements and developments can be made to maximize performance even more. From the golden era of muscle cars from the '50s to '60s, to the development of forced induction engines, turbochargers, and superchargers, there is always a desire to push performance even further. Now that EVs have been commercially available for more than a decade, with the first publicly available EV being the Tesla Roadster in 2008, certain difficulties have become apparent.
One of the most problematic parts of EVs is their batteries; the production, lifetime, and disposal of lithium-ion batteries. Furthermore, with market competition pushing the production of EVs even faster, the issues associated with lithium-ion batteries are becoming more apparent. This has lead to the creation of solid-state batteries which seek to rectify the issues associated with lithium-ion batteries.
So let's look at some of the problems with the lithium-ion battery and see how a solid-state battery will solve these issues, predicting that they will be the future of EVs.
Lesson In Lithium-Ions: What Are These Batteries?
Before we go into the differences provided by solid-state batteries, let's just do a quick refresher on standard lithium-ion batteries.
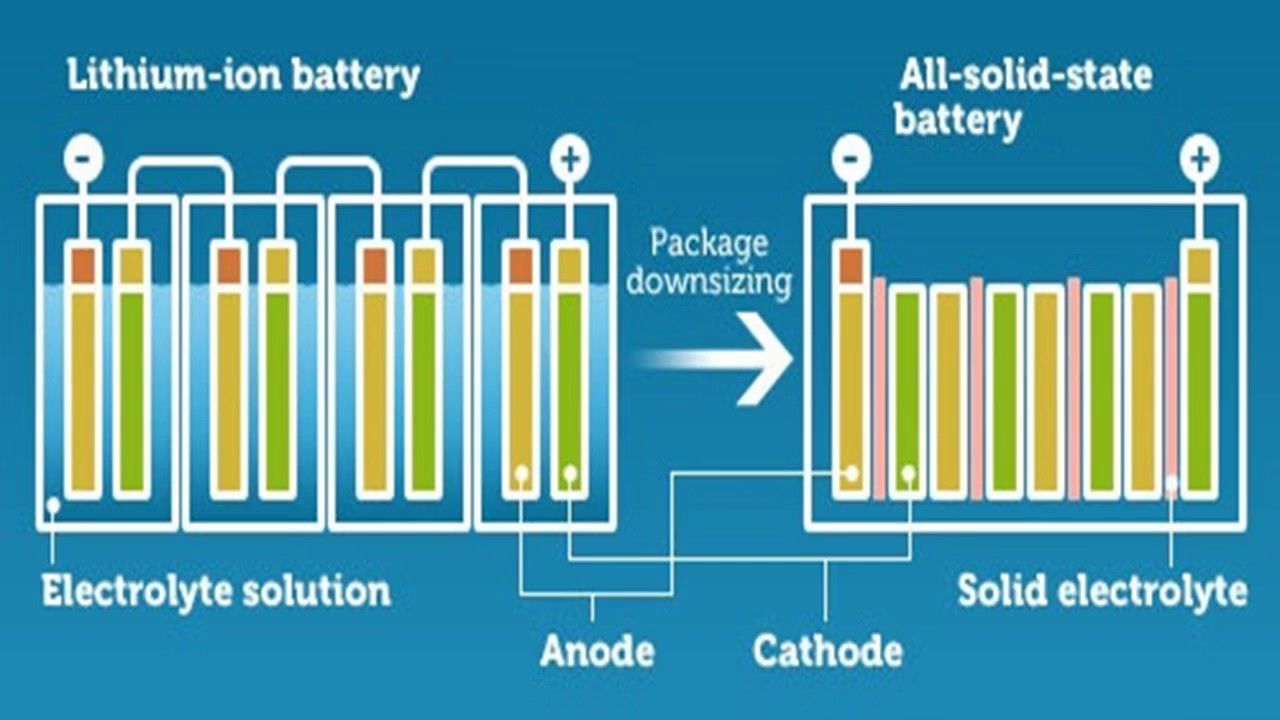
Whether you weren't paying attention in Year 10 chemistry or simply don't understand how lithium-ion batteries work, they are basically a form of rechargeable battery that uses an anode and cathode which stores lithium and a liquid electrolyte. Basically, the electrolyte carries positively charged lithium ions that travel from the anode to the cathode during discharge, and from the cathode to the anode during recharging. For a visual animation of this process, check out energy.com.
While there are a couple of other things involved in the process, it is sufficient to understand that energy is produced through the movement of positively charged lithium ions traveling through a liquid electrolyte. Solid-state batteries function on very much the same principle as lithium-ion batteries but utilize a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte used in lithium-ion batteries.
Advanced Advantages In The Age Of Alternative Fuels
Solid-state batteries have multiple advantages over lithium-ion batteries, making them better suited to EVs.
One of the key problems with lithium-ion batteries is that they age relatively quickly and are extremely volatile, making their life span in EVs questionable. While Tesla estimates that their batteries will last between 20 to 40 years, averaging a 5% degradation rate per 100,000 miles, this technology is simply too new, having only been around since 2008, to verify or reject these claims. Chevy, in their Bolt, are experiencing significantly greater degradation rates, averaging between 6% to 8% per 100,000 miles, demonstrating the vulnerability of these batteries. Another disadvantage of lithium-ion batteries is their volatility and flammability at high temperatures, making them require protection circuits to prevent overcharging and excessive heat.
This is where solid-state batteries come into the picture. Since they have a solid electrolyte they do not experience the same level of vulnerability that lithium-ion batteries have, which makes them charge faster, easier to transport and require less specialized protective equipment. Additionally, they can hold more electricity than their lithium-ion counterparts, meaning that their potential use in EVs would equate to greater driving distances per charge, which is a significant problem in current EVs. Furthermore, solid-state batteries also degrade significantly slower than lithium-ion batteries, making them better adept for a long-lasting EV.
Nominal Negatives That Need To Be Overcome
However, it's not all daisies and roses at the moment, as there are a couple of issues that need to be rectified before solid-state batteries can be produced commercially for EVs.
These batteries are still highly specialized, requiring specialized equipment to be constructed, making them very expensive. The high cost, eight times that of lithium-ion batteries, makes it difficult to scale up battery manufacturing to mass-production. Furthermore, there are some concerns regarding their durability as the solid electrolyte are said to be brittle and prone to breakage, as it expands and contracts during use. Additionally, real-world tests and assessments are yet to be conducted as these batteries are currently still in the experimental development phase, confining them to laboratories. Extensive testing and real-world applications could help answer a lot of the predicted issues, helping to provide solutions.
When Are These Batteries Going To Be Available?
Admittedly, this technology is still very new and the verifiable information about it remains very minimal.
However, Toyota has announced that it will invest in solid-state batteries significantly over the next few years, which really comes as no surprise considering they have more than 1000 patents for solid-state batteries. They are set to reveal a prototype vehicle that is powered purely by solid-state batteries that are said to outperform all previous EVs. Again, like with most developing technology, there is no way to give a definite date of release, however, estimations state that it will be completed by 2028 and that Toyota will unveil solid-state batteries suitable for EVs by the mid-2020s.
Admittedly, Volkswagen, Stellantis, Ford, BMW, and Hyundai have all made investments in solid-state technology, but Toyota is said to lead the charge, partnering with Japan's Panasonic Corp. Regardless, this remains a highly competitive area, with more information likely to be revealed from month to month.
Sources: HotCars, AutoBlog, Energy, Electronics-Notes, Medium and Nikkei

.jpg)