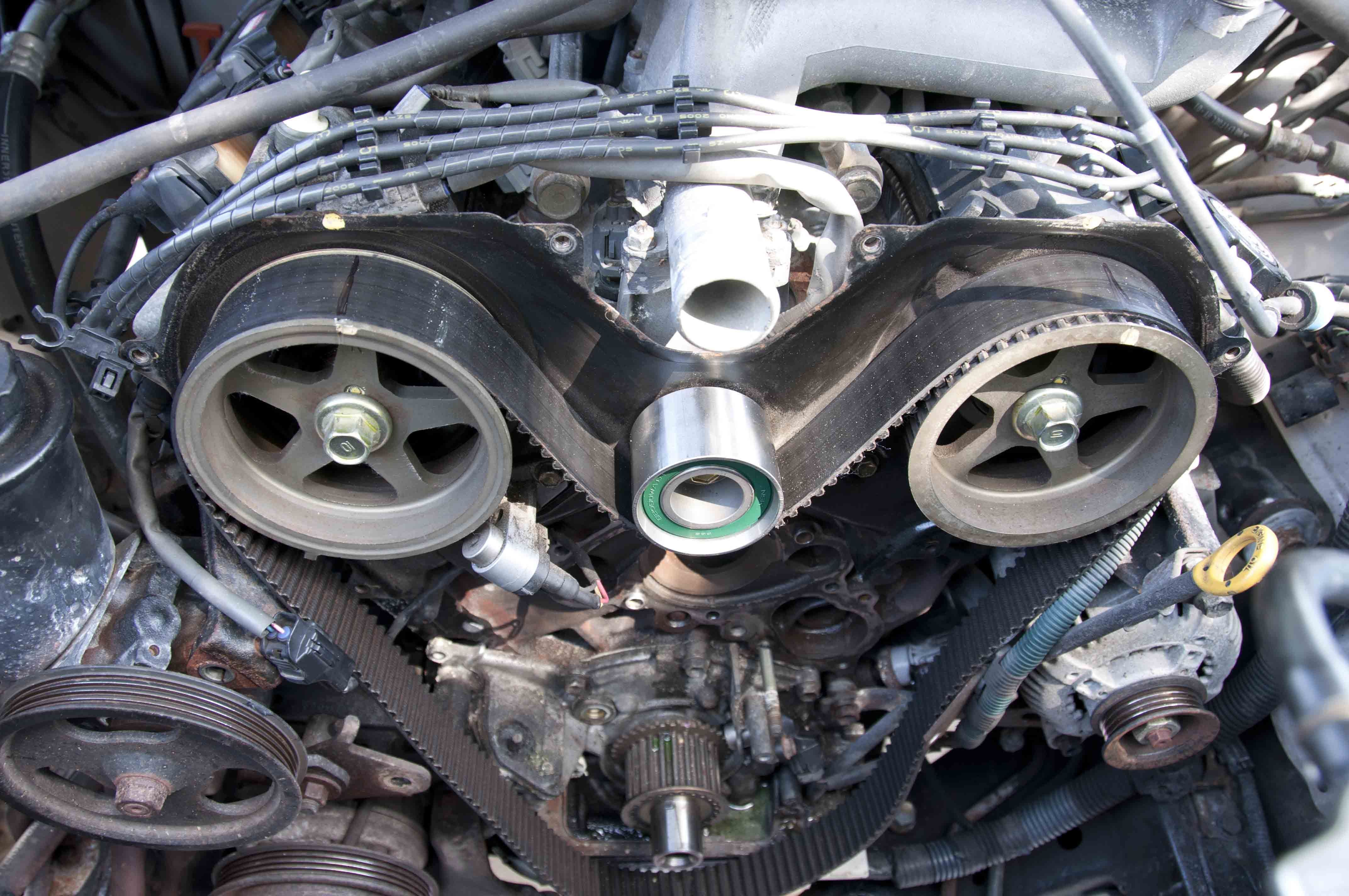
An interference engine is a type of engine in cars that produces greater power and more efficient performance through increased compression. An interference engine relies on perfectly-synchronized timing among all sorts of small parts moving in a certain sequence and in rapid succession, without any flaws along the way. A break in the timing belt can end in catastrophe, as parts stop moving, freeze, collide, and sustain damage.
Despite the potential for heavy damage, the likelihood is very low, and even lower should drivers remember to routinely replace the timing belt. Read on to find out more about the features, quirks, and advantages of interference engines.
What Are They?
"Interference Engine" may be an unfamiliar term, so it should probably be explained and explored. To start with, in a car engine, there are valves that move up and down, opening or closing intake or exhaust ports in an engine's cylinders, and they're shaped like golf tees. These movements allow the fuel and air entry into or exit from those cylinders. From there, pistons squeeze the fuel and air, causing it to ignite and power the car.
Camshafts are responsible for the moving valves, and the camshafts have belts and chains driving them. Timing is everything, so the belts and chains are called “timing belts” and “timing chains.” These belts and chains control the timing of the opening and closing of the engine's valves by driving the camshafts that power the valves.
The goal is for open valves and pistons to not occupy the same space at the same time. A piston at peak height means the valves are closed and not in the piston's path. Should everything in the engine go according to plan and operate as previously described, then everything runs smoothly.
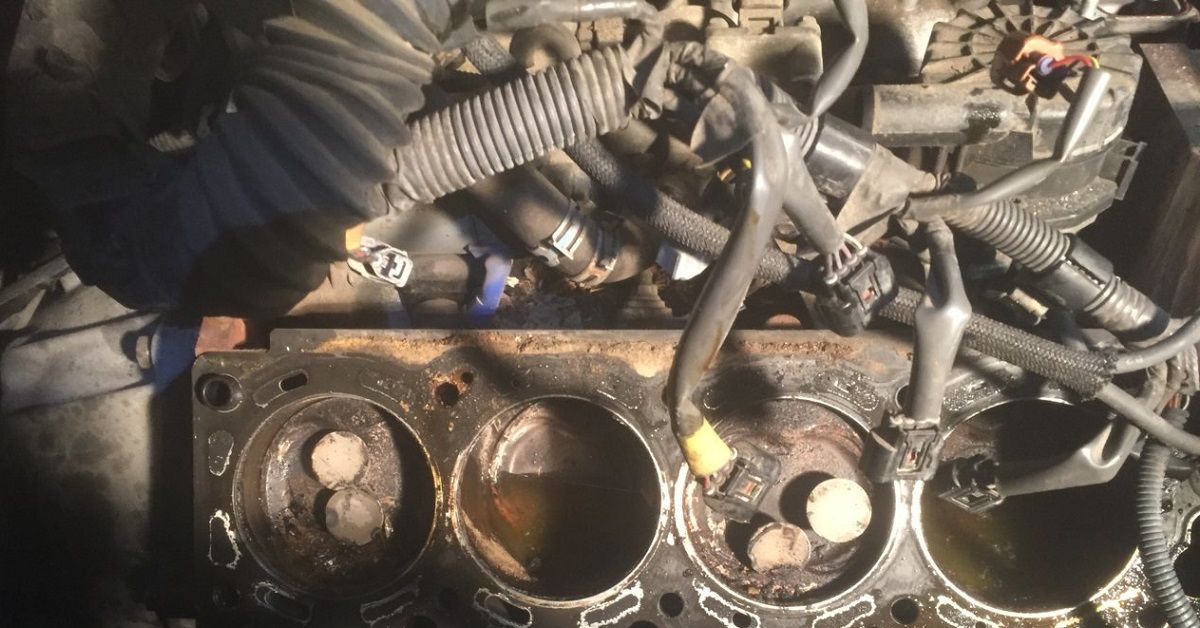
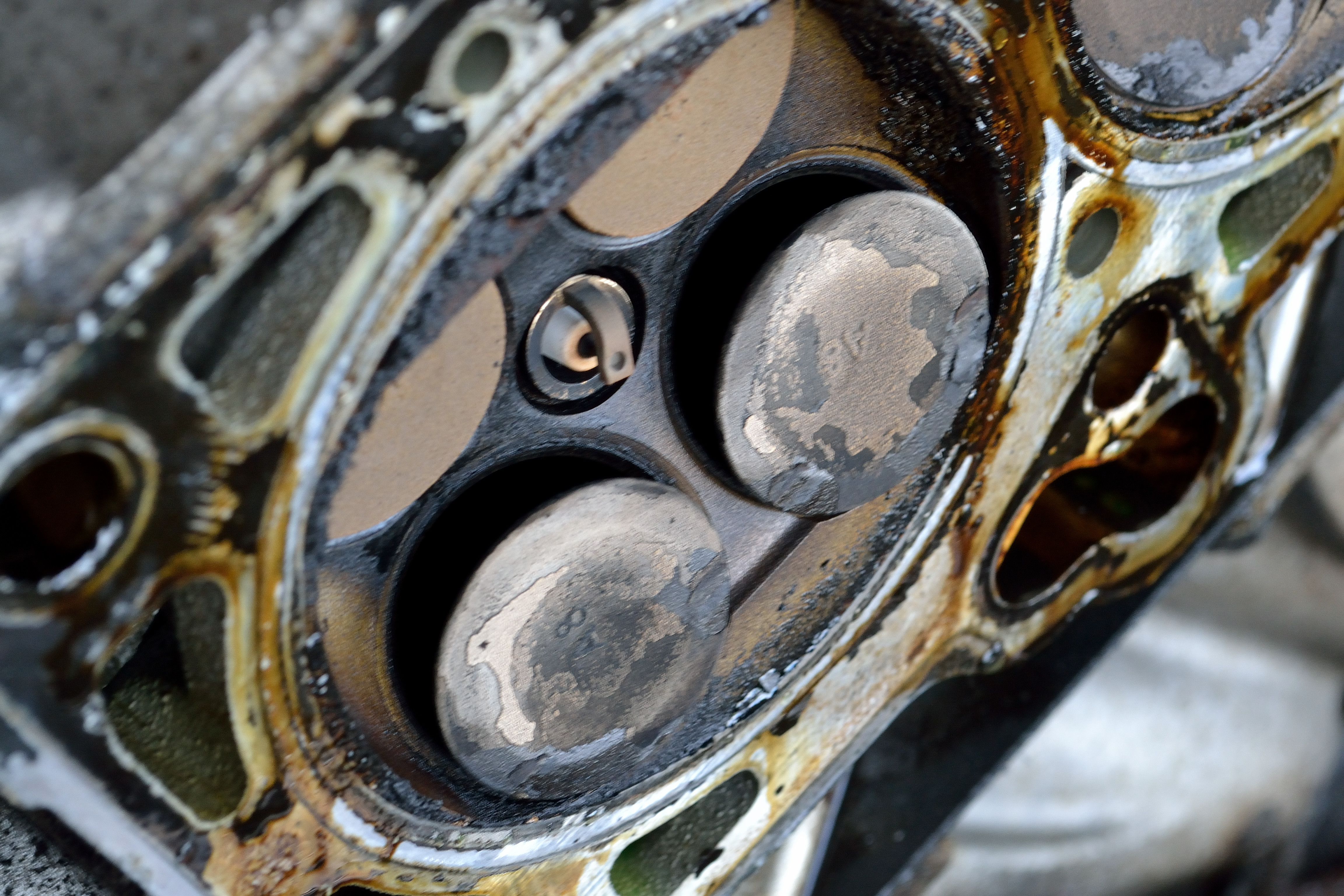
However, when the timing is no longer synchronized, disruptions occur and cause the engine to malfunction. Timing belts and chains break, disrupting the timing while the engine was running with pistons in motion. Valves can't move when the belts and chains break, so they're stuck in the position they were in when the break occurred.
Therefore, some of the valves are open. Pistons then hit the open valves, which is an interference engine. Impact from pistons causes valves to bend and break, and the pistons also sustain damage. The opposite is a free-running engine, where pistons can't get far enough to reach the valves in the first place. Interference engines are commonplace in several cars because interference engines produce high compression, which is both powerful and efficient.
Compression refers to how much of the fuel and air mixture in an engine can be squeezed, with higher squeeze rates resulting in more explosions, which result in more power. In addition, the odds of the timing belt and chain breaking and causing a disruption in timing (and subsequent damage) are slim and highly unlikely, so manufacturers opted to play the odds in exchange for greater power.
Timing Belt Is Key
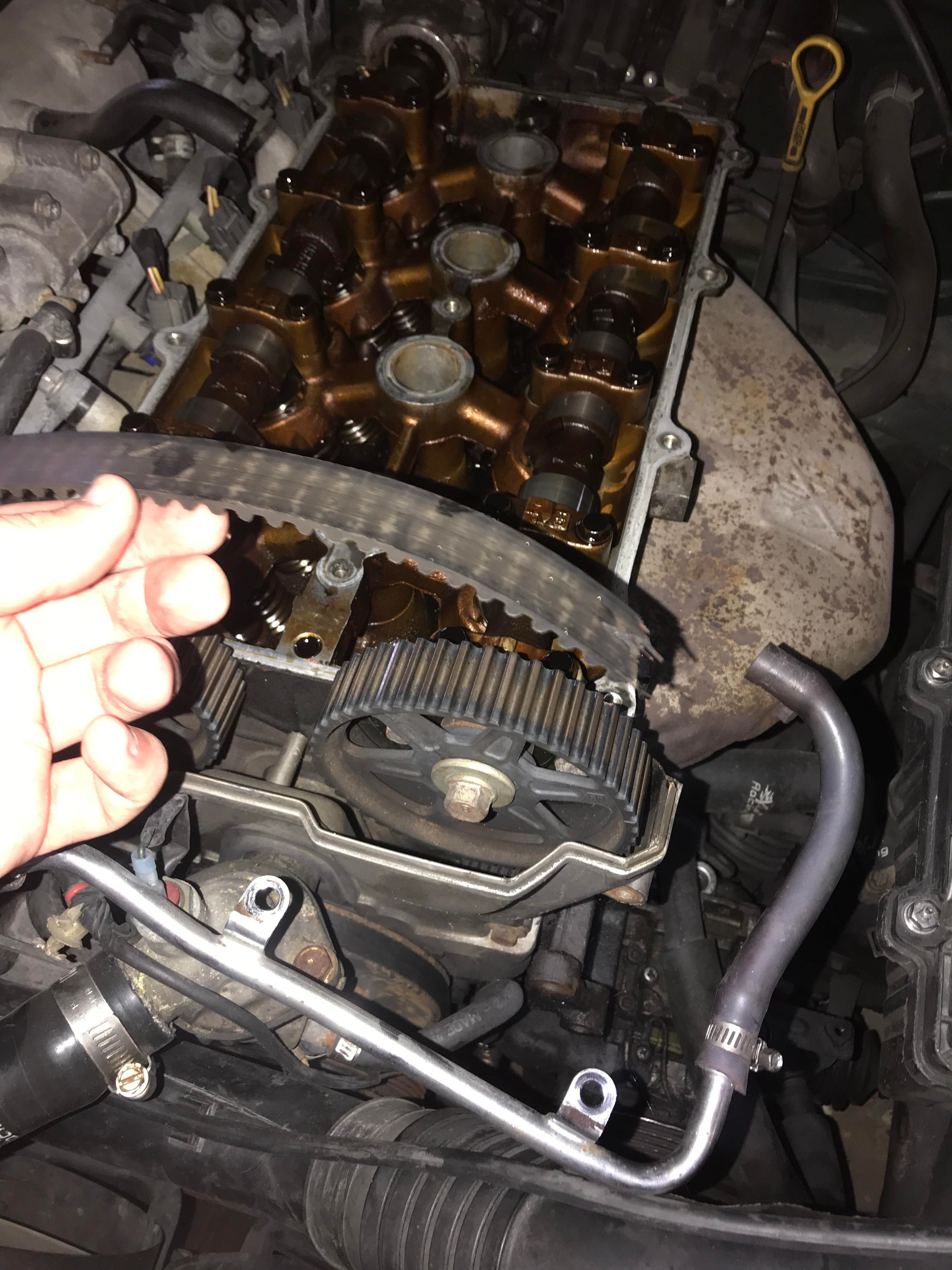
The timing belt is the most crucial piece in the entire engine setup. With free-running engines, the timing belt is not as crucial because its demise only means the engine stops and no moving parts freeze or collide, and it's a much simpler repair because no damage occurred; the only thing needing replacing is the belt itself.
A non-interference engine will just not start if a timing belt breaks; however, this scenario in an interference engine opens the possibility of parts colliding and causing heavy internal damage. It's a domino effect combined with a cascade failure should the timing belt break.
Thankfully, following a preventative maintenance schedule listed in the owner’s manual and regular replacement of the timing belt decreases the likelihood of that occurring. This is actually a good idea regardless of the engine type a vehicle has; it's just more vital to continued smooth operations in an interference engine.
Most timing belts are good for about 60,000 to 100,000 miles, so when people buy a used car and aren't sure of the timing belt's age, it's a good idea to inspect the belt for signs of wear and tear. Even if any aren't present, it may be a good idea to start fresh with a new belt at that point and note the mileage when the belt was changed. After all, simple parts perform essential functions and can keep the engine running for a long time.
Compared To Non-Interference Engines
Interference Engines have a few significant differences from their Non-Interference Engine counterparts. Design is the main point of divergence.
Interference Engines breathe better and have increased performance thanks to a higher fuel/air compression ratio. Their valves are also larger to open the combustion chamber further, thereby increasing compression and the resulting power. The combustion chamber is also smaller, aiding in more powerful compression.
Non-interference engines have the opposite setup, with smaller valves but a larger combustion chamber. This may result in less compression and less resulting power, but there's less likelihood of permanent engine damage when the timing belt breaks.
Purpose
Interference Engines were built and preferred because of certain advantages, though they have their disadvantages as well. Higher compression has long since been preferred, even since the advent of the Ford Model T, because engineers discovered the relationship between higher compression and better performance.
Diesel engines were even more reliant on higher compression, and they were more prevalent before the gasoline engines used today. Therefore, diesel engines are almost always interference engines. Advantages for an interference engine include more efficient performance, greater power, and more ventilation in the engine.
And replacing the timing belt is a straightforward enough fix to prevent damage. However, motorists need to be alert and aware of their mileage when the belt was last replaced, as the timing belt will give no warning when it fails. A chain will at least make a rattle or disruptive noise when it's about to fail; a belt does not offer this luxury.
Sources: jalopnik.com, knowhow.napaonline.com, shop.advanceautoparts.com, dannysengineportal.com,