For years, manufacturers and mad scientists the world over attempted to crack the secret wonder fuel. Everything is powering vehicles these days. Not only do gas and diesel account for most of the cars on the road, but we’re also starting to see a surge in alternative fuels.
Natural gas is just another one of these alternative fuels that entered the market to rid the world of traditional fuels. Though not as popular as hybrids or EVs, natural gas is slowly becoming a primary fuel for long-haul trucking and local transportation.
Natural gas has clear benefits, but is it the next vehicle wonder fuel? Currently, natural gas powers a little less than 200,000 vehicles in the US and almost 23 million worldwide. Here’s what we know about using natural gas as an alternative fuel.
How Is Natural Gas An Alternative Fuel?
Alternative fuel is any fuel that powers a vehicle that doesn’t use conventional gas or diesel. These fuels come in many flavors, such as hydrogen, EV, E85, biodiesel, etc. Many alternative fuels have even claimed marvelous things, but fail to produce measurable success.
One alternative fuel that is relatively unknown is natural gas. It may seem unlikely that natural gas will fall into favor with any environmental regulations. Yet, these vehicles are making a solid case as a viable alternative to conventional fuels with certain benefits.
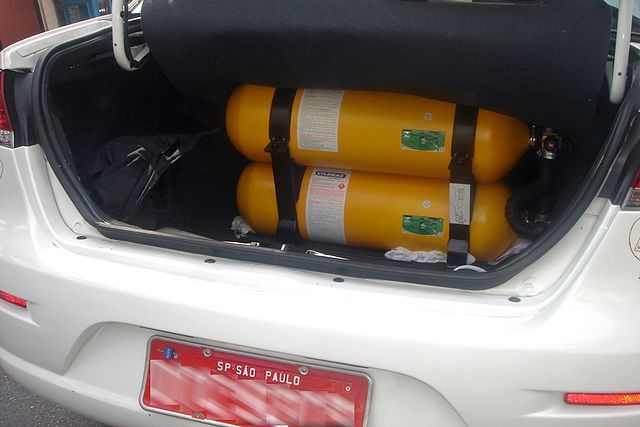
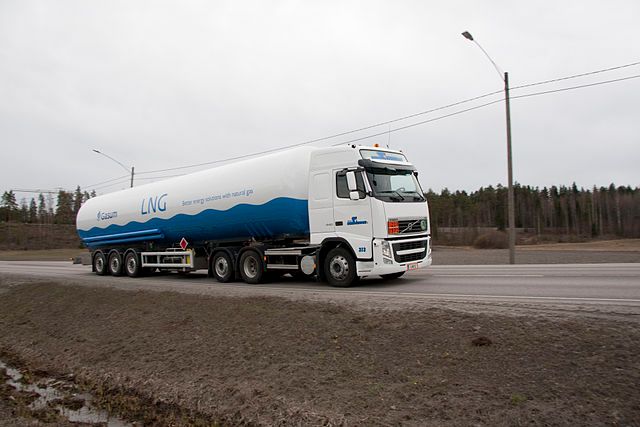
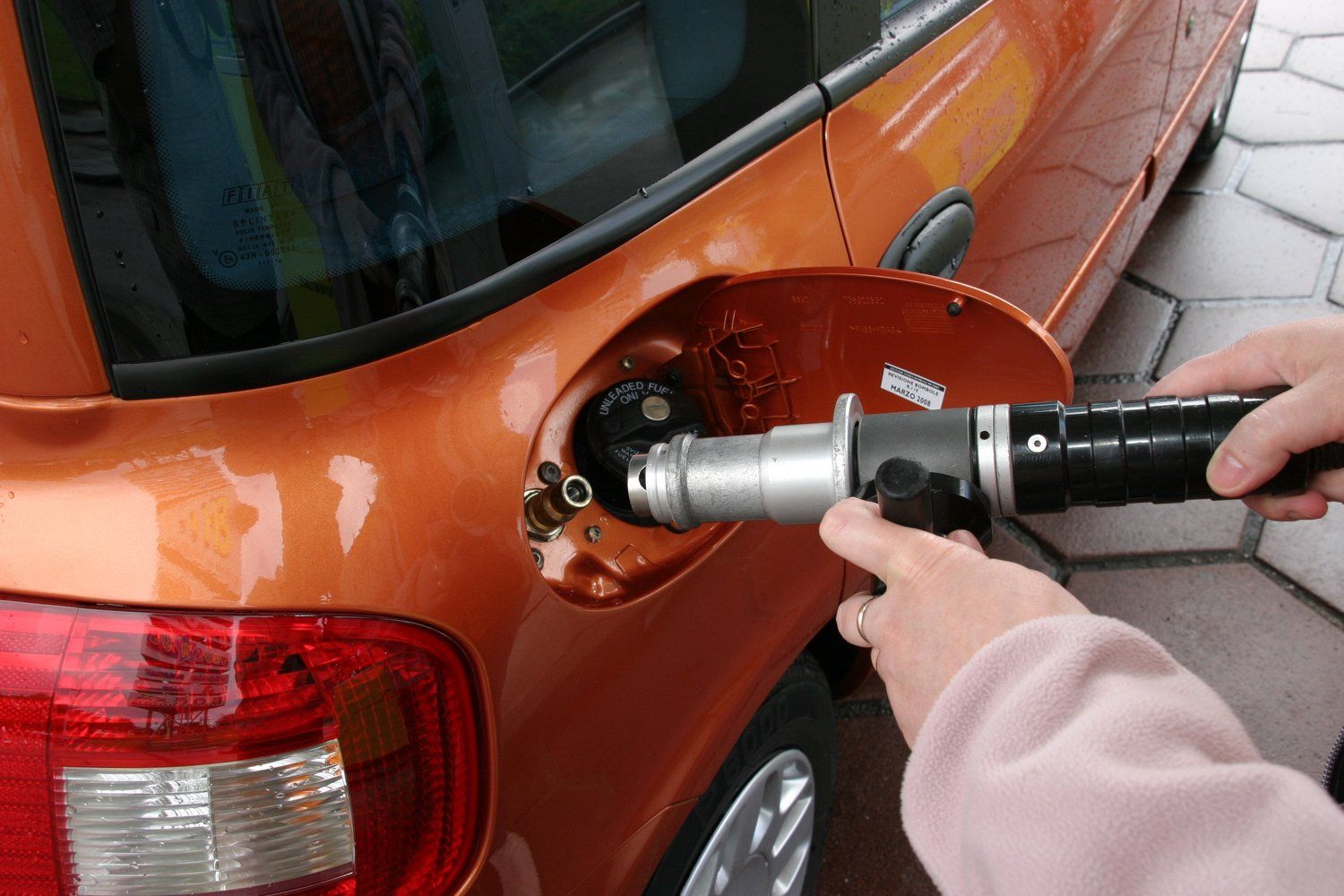
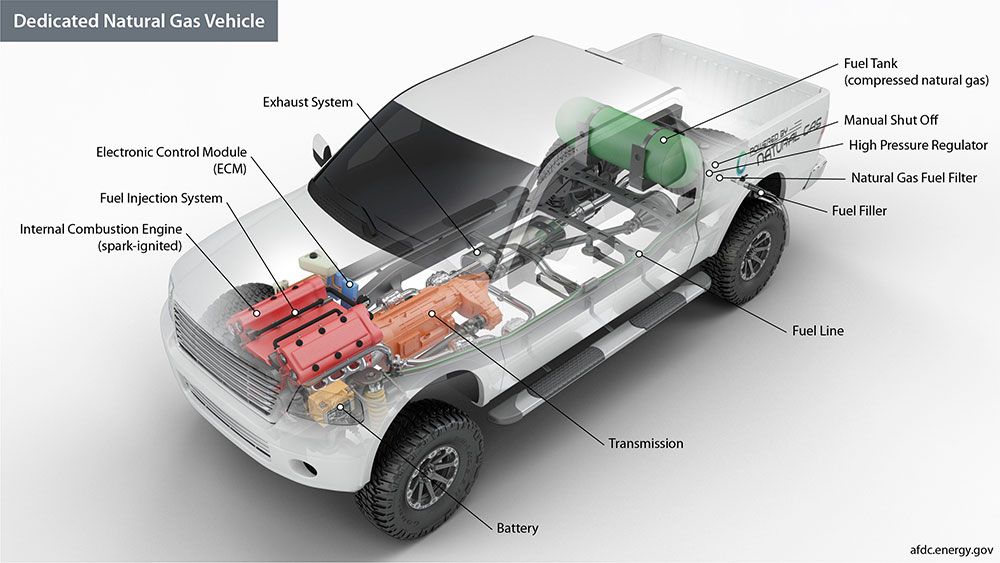
Natural gas comes in two types for powering vehicles. Compressed natural gas powers smaller, more regional operations that use a central hub for refueling. And liquefied natural gas that powers larger, long-range vehicles.
Some dedicated manufacturers produce a line of natural gas-powered vehicles, but at the moment, retrofitting is the most available option. Standard cars can be converted into dedicated natural gas vehicles using only natural gas. Additionally, a bi-fuel system uses separate fuel tanks to use both fuels. Or there’s a dual-fuel option that uses diesel to help crank the engine, then backs up to natural gas.
How Does Natural Gas Power Vehicles?
The system of powering a vehicle on natural gas functions much the same as a conventional vehicle. For instance, a fuel tank stores natural gas, either compressed or liquid. That fuel heads to the engine via fuel lines.
Once the fuel has reached the engine, pressure drops for proper ignition. Finally, the natural gas enters the combustion chamber, and the same chemical reaction takes place to liberate energy for motion.
The driver can decide which fuel to run the vehicle for bi-fuel systems. A switch is typically installed during the conversion and allows the driver to swap between the fuels. For this method, you’ll need two separate fuel tanks and lines.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Natural Gas For Vehicles?
Energy density is crucial when talking about long-distance shipping. Currently, shipping happens via trucks that rely on a central refueling network. These trucks now rely on gasoline or diesel, which is harmful to the environment, and supply chains for conventional fuels rely on international production.
Compressed and liquefied natural gas, on the other hand, has a robust system of production and distribution. As a result, domestic sources are rich in natural gas, which reduces the dependence on foreign oil.
Despite being non-renewable, natural gas provides some environmental benefits. For example, it is far less detrimental than conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel. Plus, natural gas vehicles offer the same acceleration and performance while maintaining similar ranges as traditional fuel.
Because of the low carbon, natural gas is a perfect alternative to conventional fuel. Most importantly, the system for providing fuel in natural gas vehicles is more straightforward than a traditional vehicle, which means it is easier to control emissions. When it’s easier to control emissions, cars can pass ever-stricter regulations.
Natural Gas: There’s No Such Thing As A Free Lunch
With every pro comes a con, and there are some clear disadvantages to natural gas vehicles. Natural gas is an excellent alternative to conventionally fueled cars. Still, there are limited options, such as the F-150 CNG and Leon Sportstourer TGI, and many people are unaware of even these models.
Not only are there limited options for natural gas-powered vehicles, but they’re costly as well. For instance, a conversion to CNG will run anywhere from $5,000 to $7,500 depending on the vehicle and type of retrofitting. Additionally, expect to spend the same amount higher for a new CNG vehicle, if you can even find one.
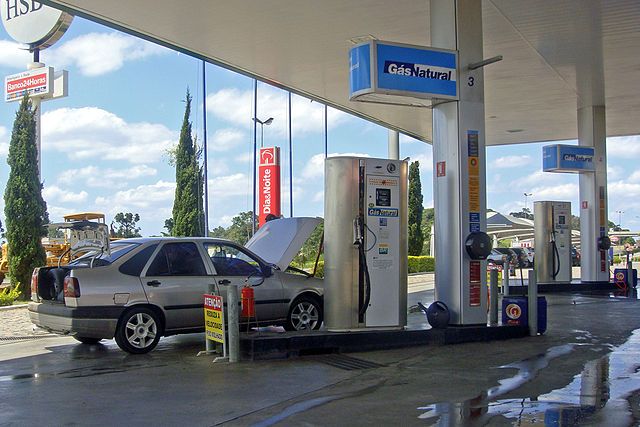
In addition to the high costs for conversion to natural gas, it’s equally expensive to fuel. There is a limited number of commercial refueling stations for natural gas, meaning you’ll need fuel shipped to the house, which is extremely expensive. Plus, refueling the natural gas takes just as long as charging an EV battery.
Finally, natural gas is a non-renewable fuel. Regardless of its advantages, there are still plenty of environmental drawbacks. As a fossil fuel, when natural gas burns, it releases fumes, which contain the same chemicals as traditional fuels. And the extraction of natural gas is just as harmful as obtaining oil.
Is Natural Gas the Next Wonder Fuel?
Probably not. But it’s a creative solution to another problem, but ultimately the reliance on non-renewable forms of energy is what we’re trying to move away from. Natural gas as a non-renewable means it’s still a form of power destined to go extinct.
Automakers try to find better ways to power vehicles, and natural gas is a solid alternative to conventional gasoline. Its benefits can’t compete, though, as hydrogen, EVs, and other forms of fuel offer similar benefits without natural gas's downsides.