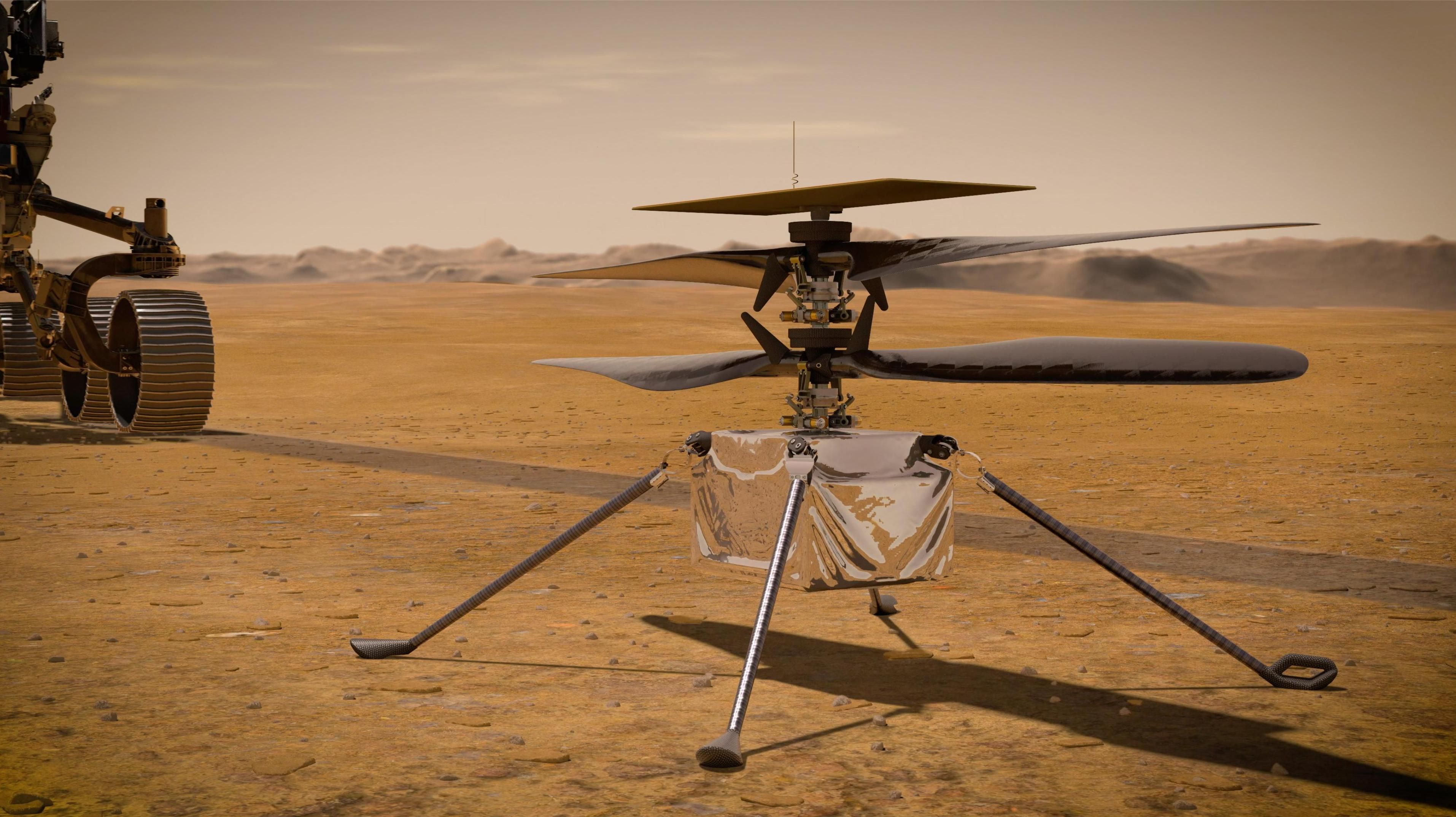
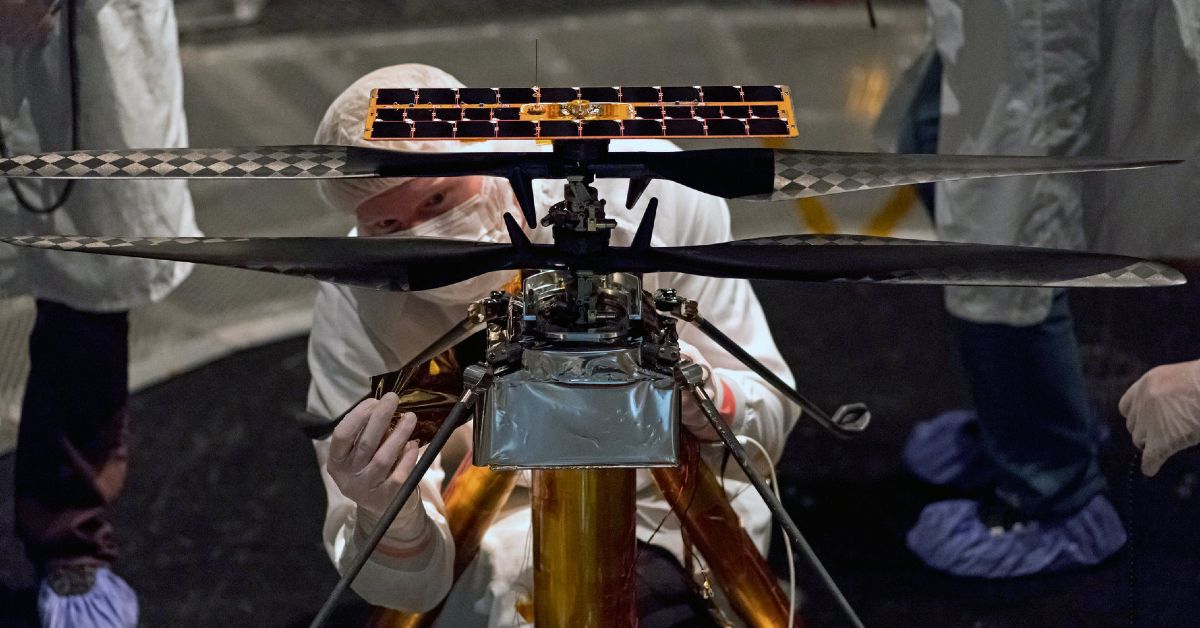
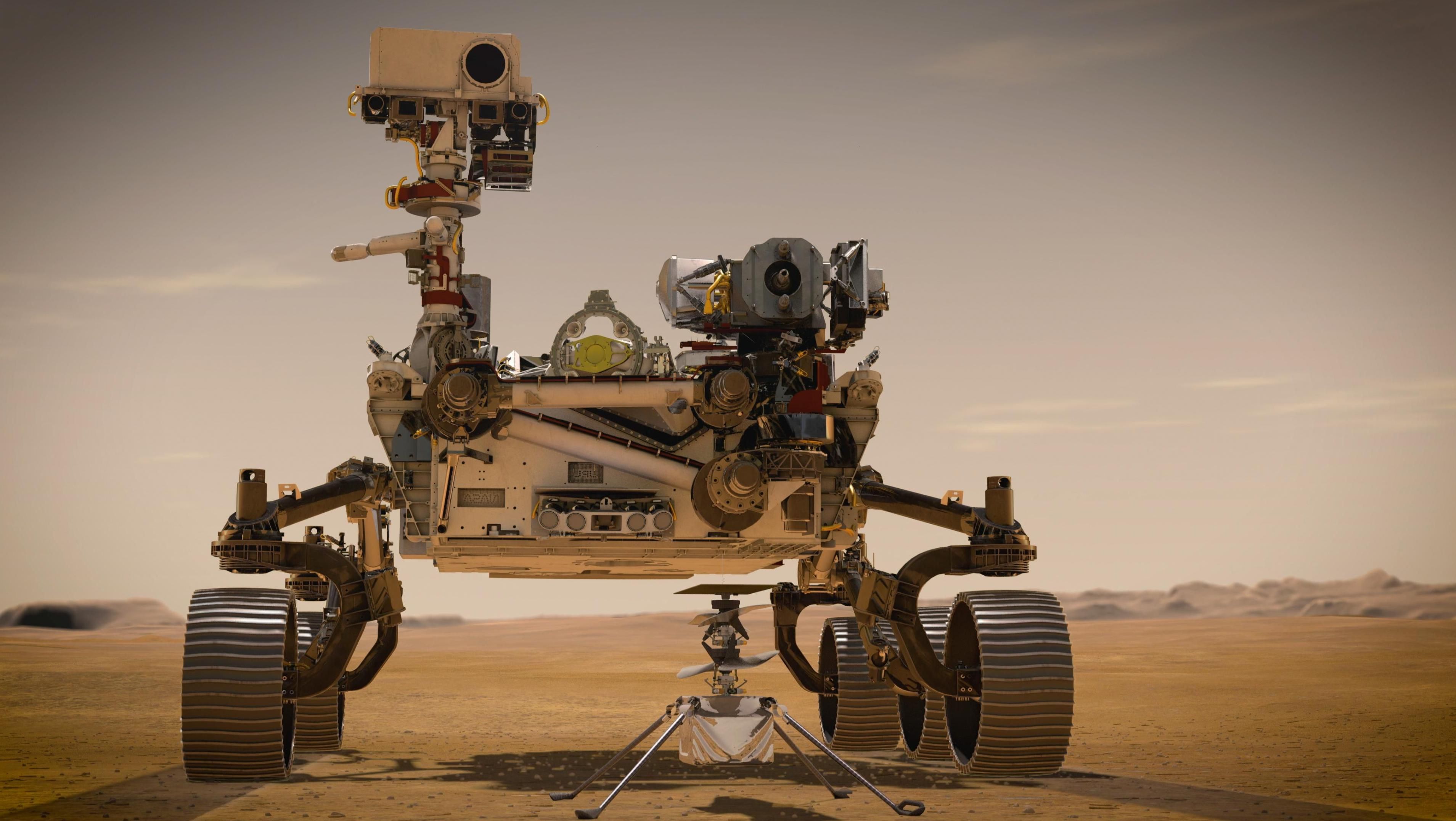
NASA's Mars Perseverance Rover has its first launch opportunity scheduled for July 30, 2020. Within the rover will be a helicopter called “Ingenuity" that will pioneer robotic flight on Mars. This helicopter will incorporate lots of interesting technology to complete its feat, as flying on Mars presents certain challenges. The first helicopter flown on Mars is engineered to complete many functions autonomously, such as charging and maintaining a safe operating temperature.
The Perseverance Rover is the largest Mars rover NASA has ever built, and it will be accompanied by lots of awesome technologies. The test flight of Ingenuity on Mars will reveal new capabilities and provide data for the creation of flight technology in the future.
Let's discover more about the Ingenuity helicopter and its impending mission in the Martian atmosphere.
3 Deployment From Mars Perseverance Rover
NASA has announced that the Mars Perseverance Rover will launch on an Atlas V Rocket with a window of July 30-Aug 15, 2020. It will make its landing on February 18, 2021 in the Jezero Crater. The rover has an undercarriage compartment from which Ingenuity will emerge, following checks to ensure correct deployment.
Although the helicopter doesn’t carry any scientific instruments, it will be testing novel solar cells and batteries as well as the craft structure itself. The first flight will likely occur about a week after the rover’s deployment to ensure that all tests have been completed.
Ingenuity will complete most of its functions autonomously with certain pre-programmed commands to assist it. One of the key functions that it must achieve is keeping itself warm, as temperatures on the Martian surface plummet to as low as -130ºF.
The craft navigates via waypoints and captures each location with a photo. Cameras and sensors provide vision for the craft and antennas allow it to communicate with Perseverance, Mars orbiters, and Earth.
2 First Helicopter On Mars
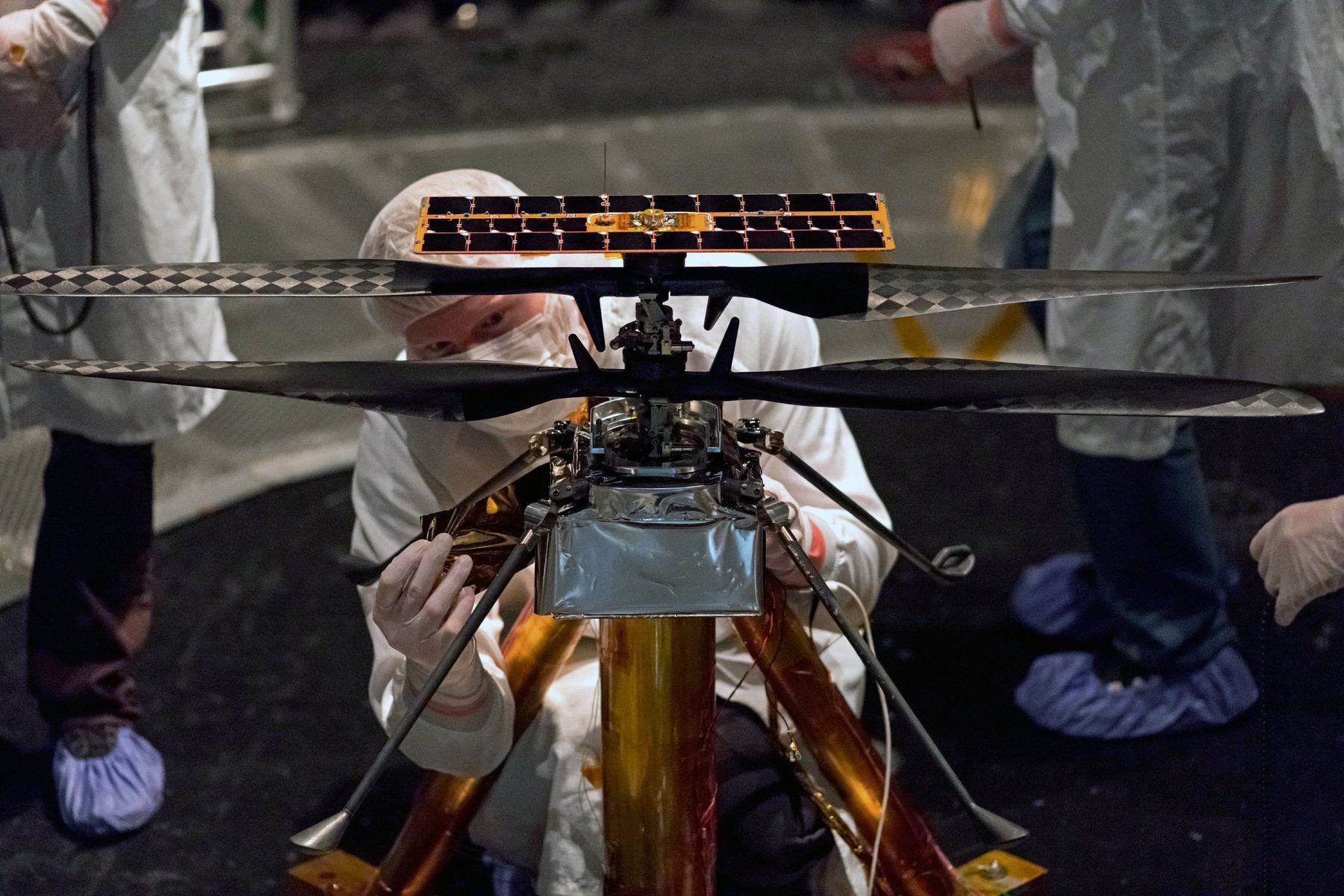
Ingenuity will be the first rotorcraft to fly on another planet. Mars has an atmosphere that is 99% less dense than that of the Earth and about 1/3 of the gravity we typically experience. Due to the difficult atmosphere on Mars, engineers had to implement unique considerations in their design. The entire structure and electronics weigh a mere 4 pounds (which is about 1.5 pounds on Mars).
The blades, which span 4 feet, are composed of a lightweight foam core surrounded by carbon fiber. "Carbon composite layups with a foam core matrix were used to achieve lightweight but stiff blades", said Ingenuity chief engineer Dr. Bob Balaram. The two rotors are contra-rotating and spin at 2,400rpm. According to NASA, the helicopter has a flight time of up to 90 seconds while hovering 10-15 feet off the ground. It consumes approximately 350 watts of power per 980-ft. flight.
1 Future Flights In The Martian Sky
The test flight of Ingenuity will be of critical importance to future Mars missions. Although the helicopter will take unique aerial pictures of the terrain, scientists will place an emphasis on the flight mechanics for this mission. Flight parameters will be increasingly ambitious after each attempt, fully verifying that each step is complete and the systems are operating properly.
The engineers and scientists will gain much information from the test flights and an enhanced ability to plan future aerial exploration on Mars. “We’ll be learning all along the way, and it will be the ultimate reward for our team to be able to add another dimension to the way we explore other worlds in the future”, said Ingenuity project manager Mimi Aung. It is likely that we will see autonomous aerial robotics playing a major role in future NASA missions. The Ingenuity project will pave the way for exploration that transcends traditional obstacles.
Sources: NASA, JPL, Space, Forbes